Ever feel stuck choosing between vectorizing and upscaling your AI art? You're not alone! 'To vectorize or not to vectorize?'—that's the big question. Today, we're going to clear up the confusion. Let's break down when to use a vectorizer versus an upscaler and find out the pros and cons of each!
Understanding the Basics
Before we explain the pros and cons, let's grasp the essence of vectorization and upscaling process. Both techniques aim to increase the quality of low-resolution images commonly produced by AI generators.
If you're planning to print your artwork on a t-shirt or display it on a larger canvas – enhancing the quality is crucial.
Either tool can be used in most cases; using both is typically unnecessary. Specific scenarios exist where one might be more suitable than the other. The choice depends on your design process, editing needs, and familiarity with each tool.
Vectorization: Unveiling the Power of Vectors
What Are Vectors?
Unlike raster images composed of pixels, vectors rely on paths and points to create designs. This fundamental difference sets vectors apart, offering scalability without sacrificing quality.
Pros of Vectorization
- Infinite Scalability: Vectors excel in scalability, allowing you to resize your artwork without loss of quality, crucial for printing large-format designs.
- Editing Capabilities: With vectors, you gain access to versatile editing tools, enabling precise modifications and color adjustments.
- Versatile File Formats: From SVG to EPS, vectors can be easily converted into various file types, facilitating seamless integration into different platforms and products.
- Smaller File Sizes: Despite their scalability, vector files maintain a smaller size compared to upscaled raster images, ensuring efficient storage and handling.
Suitable Applications for Vectorization
Not all images are equal, so understanding when to use vectorization is key. Vectors shine brightest in scenarios involving flat illustrations and 2D designs, ideal for digital artwork and simplistic graphics.
Cons of Vectorization
- Detail Loss: Highly detailed photographic images may lose detail and appear flat and simplistic.
- Gradient Distortion: Vectors struggle with preserving gradients, often breaking them into segments instead of maintaining smooth transitions.
- Limitations on Seamless Patterns: Creating seamless patterns with vectors may result in inaccuracies along the edges, compromising the seamless effect. Avoid it for pattern designs.
- File Conversion: Many print-on-demand platforms do not accept vector files, requiring conversion back to PNG, adding an extra step.
Upscaling: Enhancing Raster Images
Unveiling the Upscaling Process
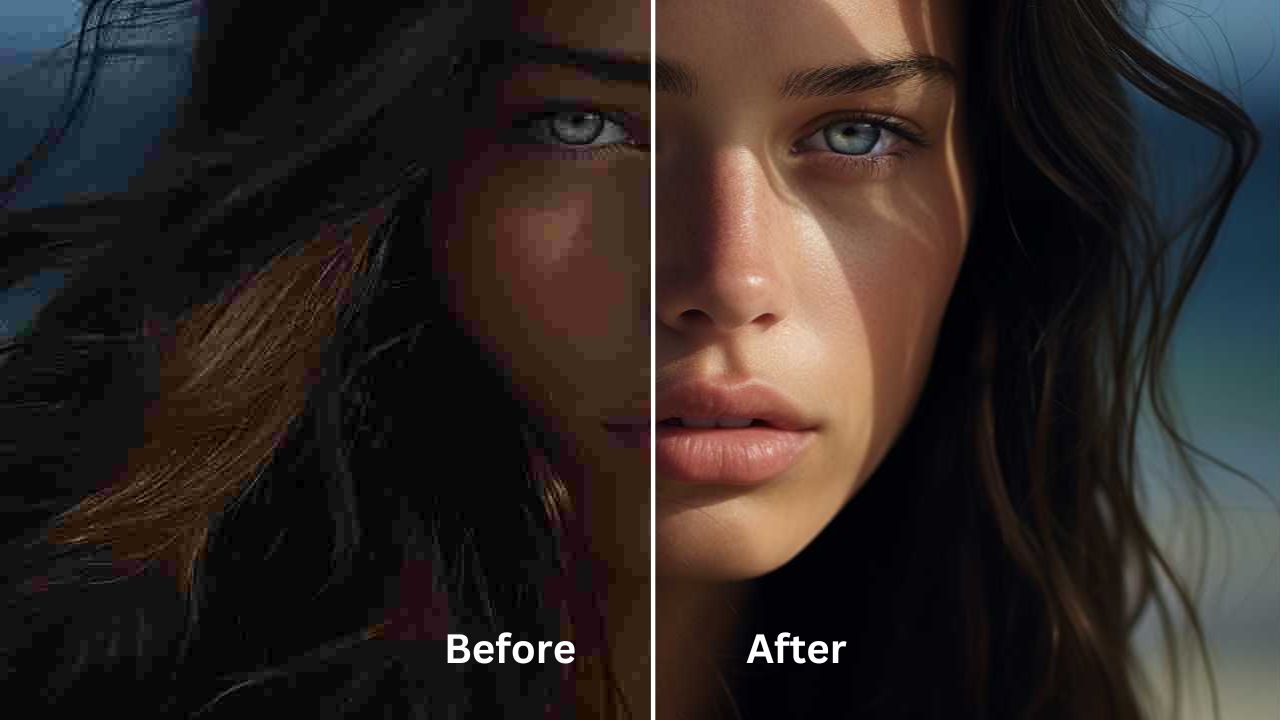
Upscaling transforms low-resolution raster images into high-quality counterparts, enhancing sharpness and detail for improved visual impact.
Pros of Upscaling
- Preservation of Original Aesthetic: Unlike vectorization, upscaling retains the original style and nuances of the artwork, ensuring authenticity.
- Pattern and Gradient Integrity: They maintain seamless patterns and gradients, ensuring design consistency and detail preservation.
- Suitability for Detailed Artwork: Upscaling excels in handling intricate designs and photography, making it an ideal choice for detailed artwork.
TIP: Upscale your image by a factor of 4 for digital use or printing. If you require further editing, upscale the image first and then use vectorize conversion!
 Online Upscaler:
Img2Go
Online Upscaler:
Img2Go
Cons of Upscaling
- "Ghosting" Effect: Upscaled images may exhibit ghosting effects around edges, resulting in a foggy or blurry appearance, particularly noticeable in certain cases.
- Increased Graininess: Upscaling can introduce graininess to images, especially evident in areas with high contrast or fine details.
- Limited Editing Capabilities: Upscaled images lack the flexibility of vectors, limiting editing options and requiring reliance on raster-based editing tools.
- Larger File Sizes: The files generated by upscaling can be excessively large. The large file sizes can slow down design tools and may not be accepted by some marketplaces due to file size restrictions.
Vectorization vs. Upscaling
In summary, both vectorization and upscaling techniques effectively enhance the quality of low-resolution AI art. Each method has its advantages and drawbacks, but there's no need to fret over choosing between them. Experimentation is key – try both approaches to see which better suits your workflow and artistic style.
If you frequently work with vectors and prefer a more digital aesthetic, a vectorizer might be the way to go. Conversely, if you often deal with photography and utilize photo editing tools like Photoshop, an upscaler may be more suitable.
Ultimately, the decision hinges on your specific needs and the type of artwork you create. Opt for the tool that best elevates the quality of your AI art.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Can I Combine Vectorization and Upscaling for Optimal Results?
While technically feasible, combining both techniques may not always yield significant benefits and could complicate the workflow unnecessarily. It's best to choose the method that best suits your specific needs.
How Do I Address Graininess in Upscaled Images?
To mitigate graininess in upscaled images, experiment with different upscaling algorithms and settings. Additionally, post-processing techniques such as noise reduction can help refine the final output.
Can I Print Vectorized Artwork on Various Merchandise Products?
Yes, vectorized artwork can be easily adapted to different merchandise products by exporting them to compatible file formats such as SVG, EPS, PDF, or PNG, ensuring versatility in printing options.
What Resolution Should I Aim for When Upscaling AI-generated Images?
The optimal resolution for upscaling AI-generated images depends on the intended use and printing requirements. Aim for a resolution that maintains visual fidelity while accommodating the desired output size. For applications like printing on t-shirts or other merchandise, higher resolutions, ideally around 5,000 to 6,000 pixels, are preferable.

